Hunyi:A Symbol of Ancient Chinese Astronomy
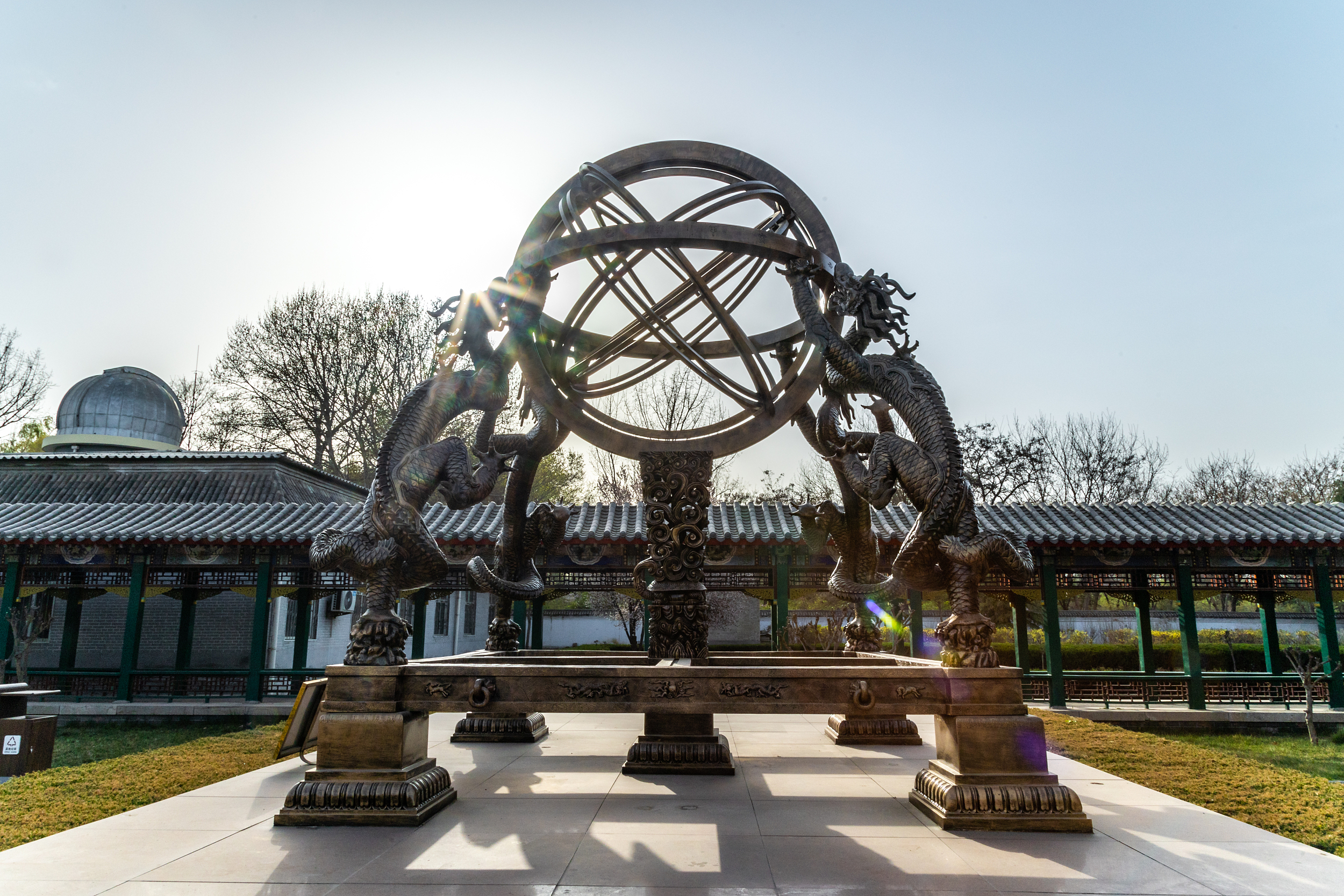

A model of Hunyi is on display at Guo Shoujing Memorial Museum in Xingtai city, Hebei province. (PHOTO: VCG)
By?BI?Weizi
Editor's Note:
The spirit of innovation and scientific thinking embedded in the 5,000-year-old Chinese civilization have shone brightly in various fields such as astronomy, geography, agriculture, medicine and mathematics.
As the saying goes, "To forge ahead into the future, one must not forget the past; to innovate better, one must be adept at inheritance." From this issue, a new series will be launched to introduce the stories of ancient Chinese inventions recorded in the book Dream Pool Essays, which reflects the highly significant sci-tech achievements of ancient China. The contributions made by Shen Kuo (1031-1095), the author, laid an important foundation for subsequent sci-tech development.
Hunyi (An armillary sphere) is an ancient Chinese astronomical instrument, which consists of a circular spherical frame centered on Earth or the Sun, representing the longitude and latitude of the celestial body and other astronomical features, such as the zodiac. The Chinese armillary sphere, based on the Armillary Theory, is the symbol of ancient Chinese astronomy.
According to the Armillary Theory, the sky is round and shaped like an egg shell. The stars are projectiles embedded in the eggshell, with Earth being the yolk. Therefore, this instrument for observing the position of celestial bodies is named Hunyi, where Hun means a ball in Chinese.
According to the ancient book on Chinese science, Dream Pool Essays, the Hunyi sphere is a miniature representation of celestial objects in the sky, consisting of a series of concentric rings centered around a globe. The relative position of the rings could be adjusted to reflect the precession of the equinoxes and the regression of the lunar nodes along the ecliptic. The hollow tube in the innermost ring, called the sighting tube, is used to point at the object of observation.
Hunyi can be traced back to the 4th century BC, about 60 years earlier than ancient Greece invented their own armillary sphere. During the Tang Dynasty (618 -907), an astronomer named Li Chunfeng designed a relatively sophisticated armillary ecliptic instrument. This was followed by the instrument being improved during the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368), by Guo Shoujing, an influential astronomer in Chinese history, to establish the location of celestial bodies and the angles of the sun relative to Earth more accurately. The earliest existing armillary sphere in China was made in the Ming Dynasty (1368 -1644) and is on display at the Purple Mountain Observatory in Nanjing.